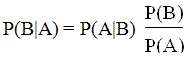
Bayes Theorem
For any two propositions, A and B, P(B|A) = P(A|B) x p(B) / p(A), where you read 'PP(A)' as "the probability of A", and 'P(A|B)' as "the probability of A given that B has occurred".
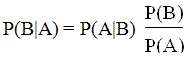
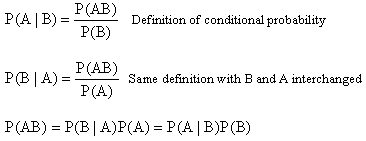
As shown, Bayes rule follows directly from the definition of conditional probability. This theorem is a way to translate between the probability of causes, given effects and the probability of effects given causes.